Dr Tchouakui and team observed that Clothianidin induces very low mortality of mosquitoes when using absolute ethanol or acetone alone as solvent. At the end of the study, they recommend monitoring the susceptibility to clothianidin using acetone + MERO at the dose of 4ug/ml.
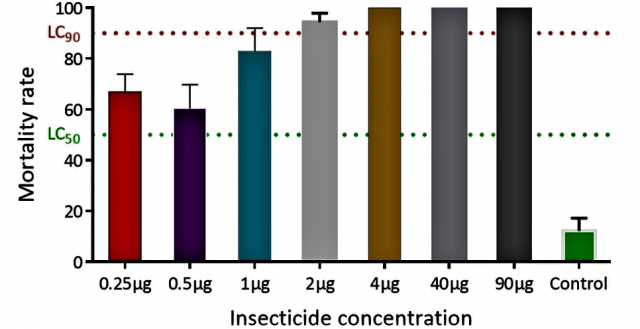
Assessment of diagnostic dose of clothianidin using acetone and MERO as solvent.
Justification of the study and results
New insecticides with different mode of action such as neonicotinoids have been recommended for public health by the World Health Organization (WHO). Unfortunately, WHO protocol to test the susceptibility of mosquitoes to neonicotinoids is not well established thus, making resistance monitoring to this insecticide class very challenging. In this study, Dr Tchouakui and team observed that Clothianidin induces very low mortality when using absolute ethanol or acetone alone as solvent. They observed for example in Nkolondom, Cameroon, a mortality rate ranging between 11.4-51.9% after exposure to this insecticide diluted in ethanol/acetone alone and 31.7- 48.2% in Mangoum (Cameroon), 34.6 – 56.1% in Mayuge (Uganda), 39.4 – 45.6% in Atatem (Ghana), 83.7 – 89.3% in Ndili (Democratic Republic of Congo). Contrastingly, they noticed that when the same insecticide was diluted in acetone + MERO, 100% mortality was observed for all the populations of mosquitoes. Similar observations were done for imidacloprid and acetamiprid. Furthermore, synergist assays with inhibitors of cytochrome P450s (Piperonyl butoxide), of Glutathion-S-transferase (Diethyl maleate) and inhibitor of esterases (DEF) revealed a significant increase of mortality after exposure to clothianidin suggesting that metabolic resistance mechanisms are contributing to the reduced susceptibility to this insecticide. Moreover, a negative association was observed between the L1014F- kdr mutation and clothianidin resistance with a greater frequency of homozygote resistant mosquitoes among the dead than the survivors. However, the I114T-GSTe2 was in contrast significantly associated with a greater ability to survive clothianidin with a higher frequency of homozygote resistant among survivors than other genotypes. At the end of this study, Dr Magellan Tchouakui recommends monitoring the susceptibility to clothianidin using acetone + MERO at the dose of 4 µg/ml to capture the accurate resistance profile of the mosquito populations as acetone or ethanol alone could overestimate the level of resistance.

Dr Magellan Tchouakui working in the Insectary
A specific process
To carry out this study, mosquitoes were collected from May to July 2021 at Njombe-Penja, Nkolondom, and Mangoum known as three agricultural settings in Cameroon and also in Ndjili-Brasserie, Democratic Republic of Congo; in Obuasi, Ghana; and in Mayuge, Uganda. Using the Centre for Disease Control (CDC) bottle test, they compared the effect of three different solvents (ethanol, acetone, MERO) on the efficacy of neonicotinoids against the Major African Malaria vector Anopheles gambiae s.l. In addition, TaqMan assays were used to genotype key pyrethroid-resistant markers in alive and dead mosquitoes and odds ratio based on Fisher exact test were used to evaluate potential cross-resistance between pyrethroids and clothianidin. Dr Magellan Tchouakui envisage to evaluate in future the susceptibility profile of field mosquitoes across Africa to Clothianidin at the dose of 4 µg/ml which was found as a diagnostic concentration with acetone + Mero.
Tchouakui M, Assatse T, Mugenzi LMJ, Menze BD, Nguiffo-Nguete D, Tchapga W, Kayondo J, Watsenga F, Manzambi EZ, Osae M, Wondji CS. Comparative study of the effect of solvents on the efficacy of neonicotinoid insecticides against malaria vector populations across Africa. Infect Dis Poverty. 2022 Apr 25;11(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40249-022-00962-4. PMID: 35462556; PMCID: PMC9036736.